Deep Learning from Scratch - Back Propagation (2)
Affine/Softmax Layer
Affine
신경망의 순전파 때 수행하는 행렬의 곱은 기하학에서 어파인 변환(affine transformation)이라고 한다.
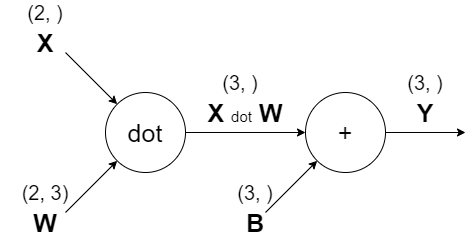 역전파에 대하여 행렬을 사용한 역전파도 행렬의 원소마다 전개해보면 스칼라값을 사용한 지금까지의 계산 그래프와 같은 순서로 생각할 수 있다. 실제로 전개해보면,
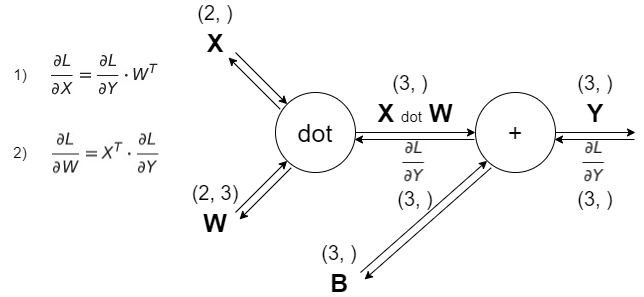
역전파에 대하여 행렬을 사용한 역전파도 행렬의 원소마다 전개해보면 스칼라값을 사용한 지금까지의 계산 그래프와 같은 순서로 생각할 수 있다. 실제로 전개해보면,
$\frac{\partial L}{\partial X} = \frac{\partial L}{\partial Y} * W^{T}$
$\frac{\partial L}{\partial W} = X^{T} * \frac{\partial L}{\partial Y}$
이를 계산그래프로 나타내보면
import numpy as np
from functions import *
class Affine:
def __init__(self, W, b):
self.W = W
self.b = b
self.x = None
self.dW = None
self.db = None
def forward(self, x):
self.x = x
out = np.dot(x, self.W) + self.b
return out
def backward(self, d_out):
dx = np.dot(d_out, self.W.T)
self.dW = np.dot(self.x.T, d_out)
self.db = np.sum(d_out, axis=0)
return dx
Softmax-with-Loss
class SoftmaxWithLoss:
def __init__(self):
self.loss = None
self.y = None
self.t = None
def forward(self, x, t):
self.t = t
self.y = softmax(x)
self.loss = cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t)
return self.loss
def backward(self, d_out=1):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
dx = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size
return dx
Network
from gradient import numerical_gradient
from functions import *
from collections import OrderedDict
from dataset import load_mnist
class ReLU:
def __init__(self):
self.mask = None
def forward(self, x):
self.mask = (x <= 0)
out = x.copy()
out[self.mask] = 0
return out
def backward(self, d_out):
d_out[self.mask] = 0
d_x = d_out
return d_x
class TwoLayerNet:
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, weight_init_std = .01):
self.params = {}
self.params['W1'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(input_size, hidden_size)
self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(hidden_size)
self.params['W2'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(hidden_size, output_size)
self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(output_size)
self.layers = OrderedDict()
self.layers['Affine1'] = Affine(self.params['W1'], self.params['b1'])
self.layers['Relu1'] = ReLU()
self.layers['Affine2'] = Affine(self.params['W2'], self.params['b2'])
self.lastlayers = SoftmaxWithLoss()
def predict(self, x):
for layer in self.layers.values():
x = layer.forward(x)
return x
def loss(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
return self.lastlayers.forward(y, t)
def accuracy(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
if t.ndim != 1 : t = np.argmax(t, axis=1)
accuracy = np.sum(y == t) / float(x.shape[0])
return accuracy
def numerical_gradient(self, x, t):
loss_W = lambda W: self.loss(x, t)
grads = {}
grads['W1'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['W1'])
grads['b1'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['b1'])
grads['W2'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['W2'])
grads['b2'] = numerical_gradient(loss_W, self.params['b2'])
return grads
def gradient(self, x, t):
# forward
self.loss(x, t)
# backward
d_out = 1
d_out = self.lastlayers.backward(d_out)
layers = list(self.layers.values())
layers.reverse()
for layer in layers:
d_out = layer.backward(d_out)
grads = {}
grads['W1'] = self.layers['Affine1'].dW
grads['b1'] = self.layers['Affine1'].db
grads['W2'] = self.layers['Affine2'].dW
grads['b2'] = self.layers['Affine2'].db
return grads
Gradient Check
(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True, one_hot_label=True)
network = TwoLayerNet(input_size = 784, hidden_size = 50, output_size = 10)
x_batch = x_train[:3]
t_batch = t_train[:3]
grad_numerical = network.numerical_gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
grad_backprop = network.gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
for key in grad_numerical.keys():
diff = np.average(np.abs(grad_backprop[key] - grad_numerical[key]))
print(key + ':' + str(diff))
W1:4.151394627115514e-10
b1:2.2757432028473964e-09
W2:4.851075656265173e-09
b2:1.3920211120177496e-07
Training
epochs = 10000
train_size = x_train.shape[0]
batch_size = 100
lr = 0.1
train_loss_list = []
train_acc_list = []
test_acc_list = []
iter_per_epoch = max(train_size / batch_size, 1)
for epoch in range(epochs+1):
batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size)
x_batch = x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = t_train[batch_mask]
# back propagation
grad = network.gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
#
for key in ('W1','b1','W2','b2'):
network.params[key] -= lr * grad[key]
loss = network.loss(x_batch, t_batch)
train_loss_list.append(loss)
if epoch % iter_per_epoch == 0:
train_acc = network.accuracy(x_train, t_train)
test_acc = network.accuracy(x_test, t_test)
train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
print('Epoch {}/{}, Train_acc : {:4f}, Test_acc : {:4f}'.format(epoch, epochs, train_acc, test_acc))
Epoch 0/10000, Train_acc : 0.099350, Test_acc : 0.104700
Epoch 600/10000, Train_acc : 0.898183, Test_acc : 0.902300
Epoch 1200/10000, Train_acc : 0.921517, Test_acc : 0.924600
Epoch 1800/10000, Train_acc : 0.935717, Test_acc : 0.936200
Epoch 2400/10000, Train_acc : 0.942867, Test_acc : 0.941300
Epoch 3000/10000, Train_acc : 0.950183, Test_acc : 0.948200
Epoch 3600/10000, Train_acc : 0.954767, Test_acc : 0.951700
Epoch 4200/10000, Train_acc : 0.958150, Test_acc : 0.954900
Epoch 4800/10000, Train_acc : 0.963183, Test_acc : 0.959500
Epoch 5400/10000, Train_acc : 0.965917, Test_acc : 0.961300
Epoch 6000/10000, Train_acc : 0.969500, Test_acc : 0.965100
Epoch 6600/10000, Train_acc : 0.970433, Test_acc : 0.965800
Epoch 7200/10000, Train_acc : 0.972050, Test_acc : 0.967600
Epoch 7800/10000, Train_acc : 0.974450, Test_acc : 0.968800
Epoch 8400/10000, Train_acc : 0.975983, Test_acc : 0.967200
Epoch 9000/10000, Train_acc : 0.977067, Test_acc : 0.970000
Epoch 9600/10000, Train_acc : 0.977500, Test_acc : 0.969800
참고 : 사이토 고키, 『DeepLearning from Scratch』, 한빛미디어(2020), p147-187